Hospital billing serves as a vital healthcare element which manages the effective invoicing and reimbursement of medical services performed by hospitals together with healthcare centers. The method requires healthcare providers to conduct insurance verification followed by procedure coding to produce bills which need payment collection either from patients or insurance groups.
Hospital billing requires thorough understanding from patients and healthcare providers to process medical payments efficiently. This article discusses hospital billing practices in medical billing and demonstrates their operation together with directions for bill negotiations and payment consequences and credit implications.
What Is Hospital Billing In Medical Billing
The complex nature of hospital billing emerges from the multiple medical services institutions provide. Medical facilities must keep consistent charge documents according to Federal legislation. Hospital billing consists of three main sections that involve billing medical services from laboratories as well as medical equipment and supplies and standard hospital operational services. Hospital management chooses external medical billing services as a method to minimize errors along with payments losses. The payment model for numerous hospitals consists of fixed rates based on patient cases and daily patient stay rates. Hospitals prefer to present their medical bills to Medicare and Medicaid when a physician’s office does not bill these programs.
How Does Hospital Billing Work?
Medical facilities use the process to create payments requests for medical treatment received from healthcare practitioners and hospitals. These cover both outpatient and in-patient services. A hospital depends on its billing process to operate in the revenue cycle successfully. Hospitals perform billing operations that extend to facilities such as laboratory tests and special medical equipment along with their services to billers.
Hospital Billing Process: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
The hospital billing process involves several essential steps to ensure accurate charges, insurance claims, and patient payments. Below is a simplified breakdown of how hospital billing works:
1. Patient Registration & Insurance Verification
When a patient visits a healthcare facility, personal and insurance details are collected during registration. The hospital uses this information to:
- Confirm insurance coverage
- Determine the patient’s financial responsibility (co-pays, deductibles, or out-of-pocket costs)
2. Medical Coding & Documentation
Every service provided—diagnoses, treatments, and procedures—must be properly documented and assigned standardized medical codes, such as:
- ICD-10 codes for diagnoses
- CPT codes for procedures
These codes ensure accurate billing and compliance with insurance requirements.
3. Claims Submission to Insurance
Once medical coding is complete, a claim is generated and sent to the insurance provider. This claim includes:
- All services rendered
- The corresponding medical codes
- The hospital’s standard charges for each service
4. Insurance Review & Reimbursement
The insurance company reviews the claim based on the patient’s policy and determines the amount they will cover. Possible outcomes include:
- Full or partial payment to the hospital
- Claim denial or rejection due to missing information, policy limitations, or coding errors
5. Patient Billing & Balance Due
After insurance reimbursement, the hospital calculates the patient’s remaining balance, which may include:
- Co-pays and deductibles
- Services not covered by insurance
The patient receives a final bill detailing the amount they owe.
6. Payment Plans & Collections
If a patient struggles to pay their balance, the hospital may offer:
- Flexible payment plans
- Financial assistance programs
- Debt collection services (as a last resort for unpaid balances)
By streamlining these steps, hospitals ensure efficient billing, proper reimbursements, and clear financial communication with patients.
Does Medicare Cover 100 percent of Hospital Bills?
The federal health insurance program Medicare serves mainly United States citizens who have reached 65 years of age or possess disability-related enrollment requirements. The medical hospital costs which Medicare covers fall short of the complete bill amounts. The extent of coverage which Medicare provides each patient depends on whether they selected Medicare Part A only or Part B only or chose both plans.
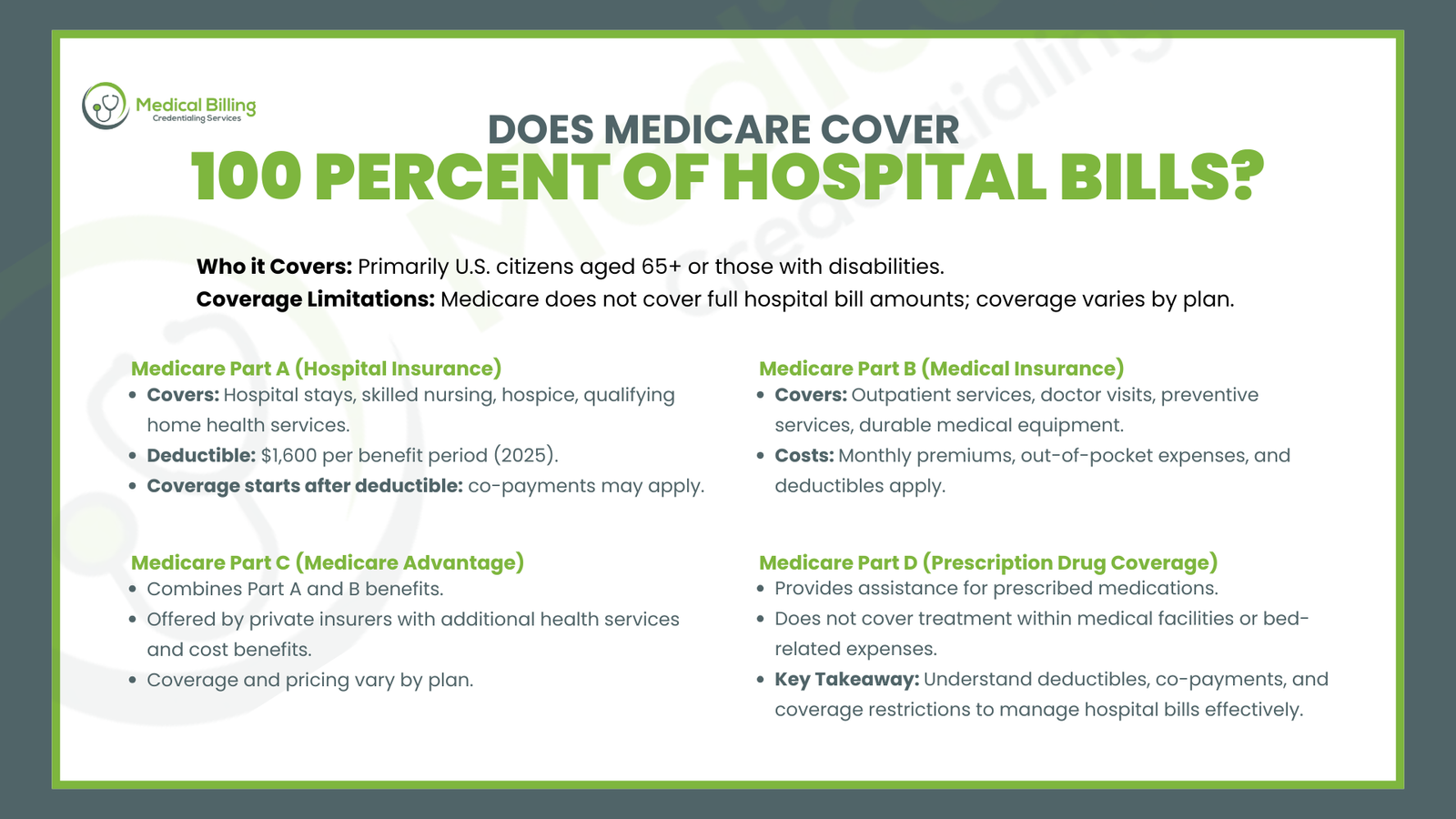
Medicare Part A (Hospital Insurance):
The Hospital Insurance provisions of Medicare Part A cover both hospital stays and skilled nursing facility treatment together with hospice care and qualifying home health services. The complete hospital bill expenses remain outside of its coverage scope. For example:
During each benefit period patients need to pay a Hospital Deductible before Medicare begins coverage for their hospital care. A medical facility stay under Medicare Part A requires a deductible payment of $1,600 in 2025. The Medicare health insurance provides full coverage for most hospital expenses after patients fulfill their annual deductible requirements yet patients still must meet select co-payment requirements related to hospital stays.
Medicare Part B (Medical Insurance):
The outpatient services covered by Medicare Part B Medical Insurance include doctor visits and preventive services along with durable medical equipment. Healthcare recipients under Part B need to pay monthly subscriptions and must handle both out-of-pocket expenses and outpatient service costs that apply to their deductible requirements.
Medicare Part C (Medicare Advantage):
Medicare Advantage programs provided by private insurers unite the Medicare Part A and Part B benefits under one package. Medicare Advantage plans from private insurers not only provide supplementary health services but also offer patients better cost-reduction benefits than patients covered through original Medicare benefits. Each Medicare health plan provides different types of coverage and sets its own pricing rates.
Medicare Part D (Prescription Drug Coverage):
Prescription Drug Coverage or Medicare Part D allows members to receive assistance with their prescribed medications. Medicare Part D provides prescription drug benefits while ignoring treatment within medical facilities along with expenses linked to beds.
The medical bill amount exceeds the level of health care coverage Medicare delivers through hospital care and services during hospital stays. All beneficiaries need to understand how deductibles work alongside co-payment amounts and coverage restrictions in their plans.
How to Negotiate Hospital Bill
Hospital bill negotiations provide patients with an opportunity to decrease their large medical expenses. Medical expenses become overwhelming for numerous patients while hospitals remain willing to settle financial matters. The following list demonstrates ways to negotiate hospital bills:
- Review the Bill Thoroughly: Examine the hospital bill before beginning any negotiations. Medical errors lead to wrong charges that belong to procedures which patients never received or which were incorrectly coded in the first place. You should obtain a detailed invoice showing all costs to assess every entry.
- Check Your Insurance Coverage: Check your insurance billing process with healthcare providers because correct billing must be verified for hospitals that process your insurance claims. Verify that all parts of your deductible and co-payment charges match correctly with the bill statement.
- Contact the Hospital’s Billing Department: After checking your billing statement is accurate review it you need to contact the hospital’s billing department. Handle billing disagreements with respect and company when discussing them with billing representatives. Request from the hospital staff to explain each charge and help you understand points that remain unclear.
You should attempt to negotiate both the discounted payment rate and payment installment plans. The hospital gives price reduction options to both patients who do not have insurance and individuals who plan to pay with cash. You may request the hospital staff to build payment arrangements if you need extra time to pay the medical bill in full. Hospital organizations will give you a reduced bill rate if you agree to make complete payment instead of monthly installments.
- Ask for Financial Assistance Programs: Financial assistance programs operated by numerous hospitals grant low-cost health care options through discount services and subsidies. Inquire about all programs that can potentially decrease your medical bill.
- Use a Medical Billing Advocate: A medical billing advocate can help simplify the billing process if you decide to hire one because you find this work too complicated. Medical billing advocates exist to help their clients obtain fair billing and negotiate reduced costs with service providers.
If You Don’t Pay A Hospital Bill What Happens
Nonpayment of hospital bills leads to significant adverse results. Extended patient timelines for payments do not prevent hospitals from remembering unsatisfied debts. The following consequences will occur when you fail to pay your hospital bill.
- Late Fees and Interest: Hospitals will implement both late fees and interest charges when patients fail to fulfill payment deadlines. The accrued charges from this practice increase your bill making payment even more challenging.
- Collection Agency Involvement: When patients do not pay medical bills or establish payment arrangements with hospitals these medical facilities typically move the bills to a collection agency. The recovery processes for collection agencies involve phone calls and letters as well as possible legal steps to regain debt amounts.
- Legal Action: Hospitals and collection agencies will resort to legal procedures to retrieve unpaid funds in case no payment is made. Wage garnishment and bank account levies and imposition of property liens become possible consequences in this situation.
- Impact on Your Credit Score: All unpaid hospital expenses will ruin your credit score adversely. When medical debt passes through collection channels your credit score decreases while future loan applications get jeopardized.
- Loss of Future Healthcare Services: Healthcare organizations will deny emergency as well as non-emergency care to patients who have an outstanding balance exceeding a certain amount unless there is an established payment agreement in place.
Do Hospital Bills Affect My Credit?
Financial obligations to hospitals have the power to impact your credit score. Persistent hospital bills that are not paid will lead to collection of the debt which results in credit bureaus receiving reports about the unpaid balance. Creditor reporting these unpaid bills will cause your credit score to decrease leading to lasting financial problems. Your ability to obtain financing would reduce because of a poor credit score while you also will probably get elevated interest rates on loans and credit.
Credit reporting agencies handle medical debts differently from standard kinds of debt. Credit reporting under the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) requires medical debts to get their own distinct category separate from other types of debt reporting. The credit bureaus are obliged to erase medical debt from your credit report after you make full payment of reported debts.
What Happens If a Hospital Bill Doesn’t Go to Collections?
A hospital bill which avoids collection activities may indicate that the hospital either cancelled your debt or permitted an extended payment arrangement or experienced delays in debt collection processes. Several health facilities extend additional payment periods for their patients while providing financial support resources. A hospital usually decides against debt collection when patients demonstrate financial incapability to pay their bills. Nevertheless the unpaid debt might later result in challenges for patients when obtaining non-emergency medical services since it affects their future healthcare access.
Conclusion
Medical establishments follow complicated procedures for processing their bills during the medical billing process. Medical billing provides proper payments to patients along with insurance firms therefore it also enables healthcare providers to handle their financial matters. The hospital costs Medicare pays for remain only partially covered as the program does not extent to full payment. Hospital patients need to examine their bills for accuracy while they should seek discounts when needed and recognize the financial problems created by non-payment. Patients can effectively control and minimize their hospital costs through appropriate communication alongside the use of healthcare payment assistance resources.
FAQs
What is the difference between a hospital bill and a medical bill?
A “hospital bill” is the name given for the medical services provided under the confines of the hospital, including the facility charges and the payments for the procedures undertaken during the patient’s visit, whereas “a medical bill” is the general name for the medical bill for the medical care provided by the medical provider under the clinic, the office of the physician, or the hospital
What does hospital billing do?
Hospital billing is the process of filing claims against insurance providers for payments for the medical treatment provided to individuals treated by the hospital, essentially taking care of the financial side of patient treatment by causing the hospital to recover for the treatment and procedures performed.
What are the two types of medical billing?
The two main types of medical billing are professional and institutional billing.
Institutional Billing is utilized by medical facilities, outpatient and inpatient facilities alike, for outpatient and inpatient services. Unique codes like UB-04 are utilized for the billing for the given services. Whereas Professional Billing is used by solo providers such as specialists or physicians for professional services billing. Professional Billing typically uses CMS-1500 forms for insurance provider filing claims. You should also see the differences of these billing types here.
How is hospital billing different from physician billing?
Hospital billing pays for the room and board facility services, while physician billing pays for medical services by the physician. UB-04 is the form for the hospital billing, and the form for physician billing is the CMS-1500.
Is hospital billing hard?
Hospital billing is made complex by the variety of services provided, the presence of multiple coding systems, insurance processes, and variety of patient demands. This requires detail, medical expertise, and insurance policy knowledge, and is not easily accomplished by those not skilled in medical billing.
Why do hospitals and doctors bill separately?
Hospitals and doctors charge separately owing to the nature of the various services each one is providing. Hospitals charge for the use of their equipment, their building, and support services like room charges, administrative expenses, and nurse care. Doctors charge for their professional work like consultations, exams, and procedures. This separation is for the purpose of each provider being remunerated for their distinctive contribution towards patient care.

